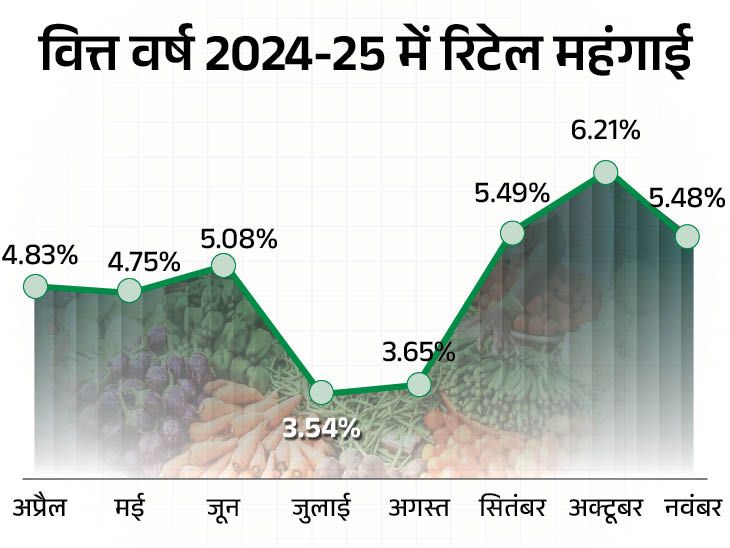
Due to cheaper food, retail inflation fell to a four-month low in December. According to government data released on Monday, inflation returned to 5.22%. Earlier in November, the inflation rate was 5.48%. Whereas 4 months ago, in August, inflation was 3.65%.
Food products contribute around 50% to the inflation basket. Its inflation rose from 9.04% to 8.39% on a monthly basis. While rural inflation decreased from 5.95% to 5.76% and urban inflation from 4.89% to 4.58%.
What is the impact of inflation?
Inflation is directly linked to purchasing power. For example, if the inflation rate is 6%, then Rs 100 earned will be worth only Rs 94. Therefore, investments should be made only keeping inflation in mind. Otherwise, the value of your money will decrease.
How does inflation rise and fall?
The rise and fall of inflation depends on the demand and supply of the product. If people have more money, they will buy more things. Buying more things will increase the demand for things and if the supply does not match the demand, the price of those things will increase.
The market thus becomes vulnerable to inflation. Simply put, an excessive flow of money or a shortage of goods in the market causes inflation. Whereas if demand is less and supply is greater, inflation will be lower.
Inflation is determined by the CPI
As a customer, you and I purchase products from the retail market. The job of showing price changes related to this is done by the Consumer Price Index, i.e. the CPI. The CPI measures the average price we pay for goods and services.
Besides crude oil, raw material prices and manufacturing costs, many other factors play an important role in determining the rate of retail inflation. There are about 300 items based on which the retail inflation rate is determined.